Attention
Note: You will need to apply to Twitter for permission before you use their API.
In this article we will discuss how to fetch the data using Twitter API in Jupyter Notebook. We will create a collection of tweets using a pre determined keyword in this project.
First of all, we need to import the libraries
Import libraries
import tweepy
import csv
import pandas as pd
import datetime
Then, we have to use the key or token given by twitter.
Use the token or key
consumer_key = "***********************"
consumer_secret = "***********************"
access_token = "***********************"
access_token_secret = "***********************"
After that we need to authenticate and verify the API by using this code :
Verify The API
# Create the authentication object
auth = tweepy.OAuthHandler(consumer_key, consumer_secret)
# Set the access token and access token secret
auth.set_access_token(access_token, access_token_secret)
# Create api object
api = tweepy.API(auth, wait_on_rate_limit=True)
Next thing, we have to determine the words that will be used as a benchmark in collecting data. In this case we will use “Julian Assange” as the keywords.
Search Key
search_key = "Julian Assange"
Then we need to decide, which way we want to store the tweets. In this case, I will use csv to store the data.
Import to csv
csv_file = open(search_key+".csv", "a", newline="", encoding="utf-8" )
csv_writer = csv.writer(csv_file)
Set the header
# Heading
date = []
tweet_id = []
tweet_user = []
text = []
Next, we have to determine the day that will be used as a benchmark for collecting the data.
Set the date
# setting datetime
today = datetime.datetime.now()
today = today.replace(hour=23, minute=59, second=59, microsecond=999999) # set from the beggining of the day
time_to_the_past = 7 # 7 because we want 1 day before today
a_week_ago = today - datetime.timedelta(time_to_the_past)
After that, we need to decide on the parameter that will be used to gather the data.
Set the parameter
# Collecting data
next_day = a_week_ago + datetime.timedelta(time_to_the_past) # equivalent to today
for tweet in tweepy.Cursor(api.search_tweets, q=search_key, count=500,
lang="en", until=next_day.date(),tweet_mode='extended').items():
print(tweet.created_at, tweet.id, tweet.user.name, tweet.full_text)
date.append(tweet.created_at)
tweet_id.append(tweet.id)
tweet_user.append(tweet.user.name)
text.append(tweet.full_text.encode("utf-8"))
tweets = [tweet.created_at, tweet.id, tweet.user.name, tweet.full_text.encode("utf-8")]
csv_writer.writerow(tweets)
csv_file.close()
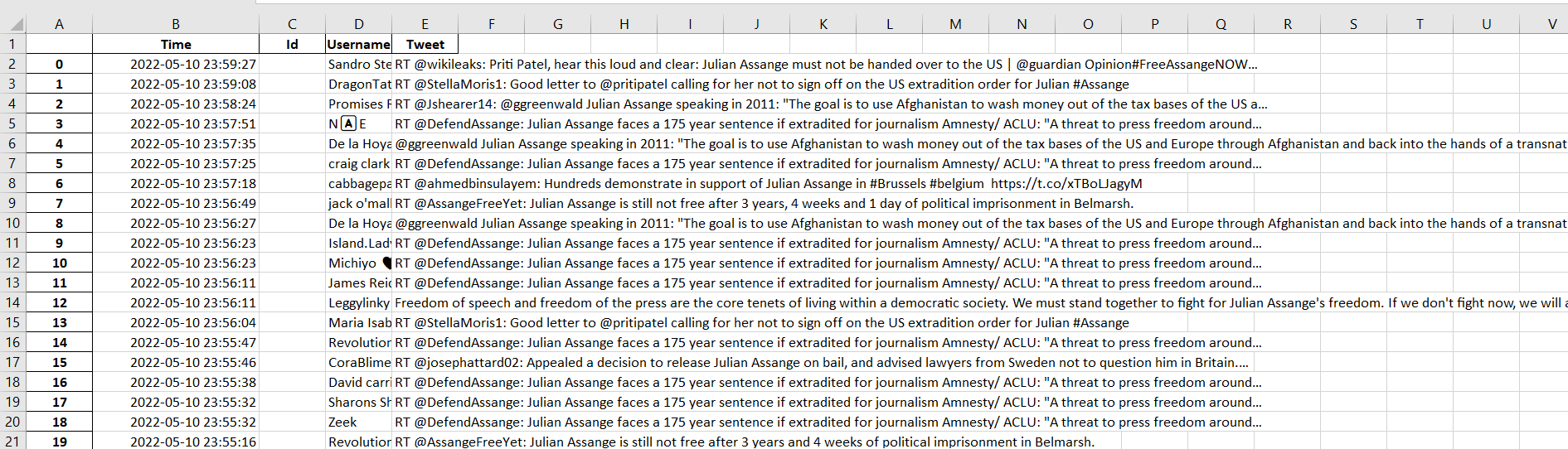
Here are some pictures from the process of gathering the data.
Gathering the data

Saving into csv

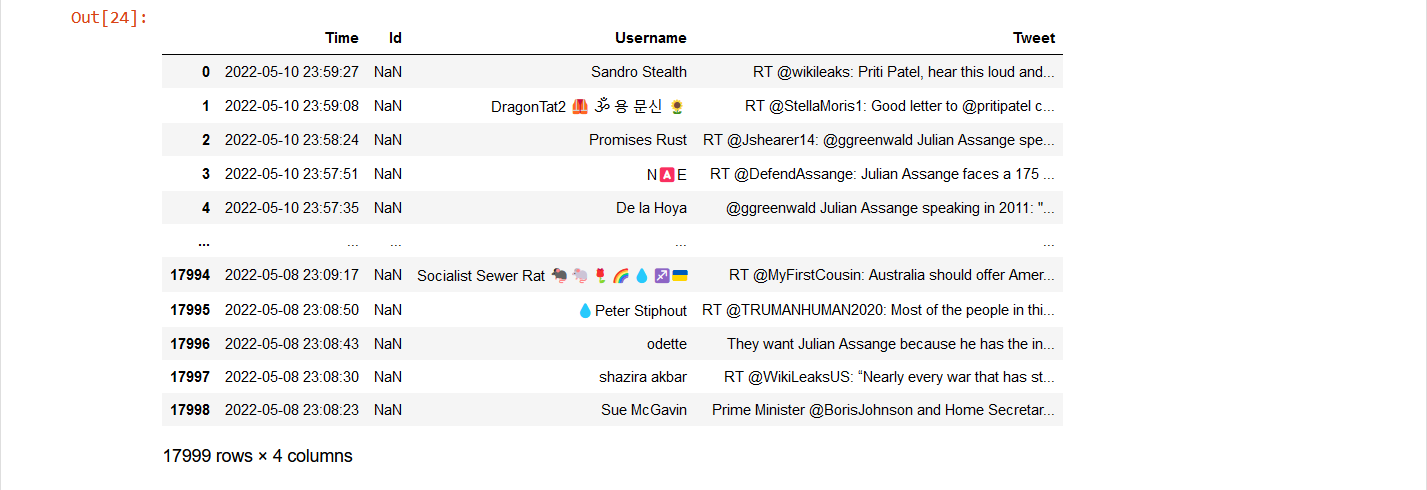
As you can see from the pictures, there are a lot of emojis that turn into characters that were saved in csv. Therefore, we need to clean the emojis so we can use the data properly.
In this case, i will turn the tweetes into dataframe and then remove the emojis from the dataframe. Here are the codes to remove the emojis
Remove the emojis
# Create dataframe
dict_tweets = {"Time":date, "ID":tweet_id, "Username":tweet_user, "Tweet":text}
df = pd.DataFrame(dict_tweets,columns=["Time","Id","Username","Tweet"])
import re
def remove_emojis(data):
emoj = re.compile("["
u"\U0001F600-\U0001F64F" # emoticons
u"\U0001F300-\U0001F5FF" # symbols & pictographs
u"\U0001F680-\U0001F6FF" # transport & map symbols
u"\U0001F1E0-\U0001F1FF" # flags (iOS)
u"\U00002500-\U00002BEF" # chinese char
u"\U00002702-\U000027B0"
u"\U00002702-\U000027B0"
u"\U000024C2-\U0001F251"
u"\U0001f926-\U0001f937"
u"\U00010000-\U0010ffff"
u"\u2640-\u2642"
u"\u2600-\u2B55"
u"\u200d"
u"\u23cf"
u"\u23e9"
u"\u231a"
u"\ufe0f" # dingbats
u"\u3030"
"]+", re.UNICODE)
return re.sub(emoj, '', data.decode('utf-8'))
df['Tweet'] = df['Tweet'].apply(remove_emojis)
Here is a picture of the dataframe data that has been processed.
Cleaned dataframes
After we clean the emojis, we need to store the clean tweets from the dataframe. In this case, I will store it in Excel’s form
Saving into excel
df['Time'] = df['Time'].dt.tz_localize(None)
df.to_excel('Julian.xlsx')
Here is the picture of the tweets that is stored in Excel’s form